|
Gel Electrophoresis Notes
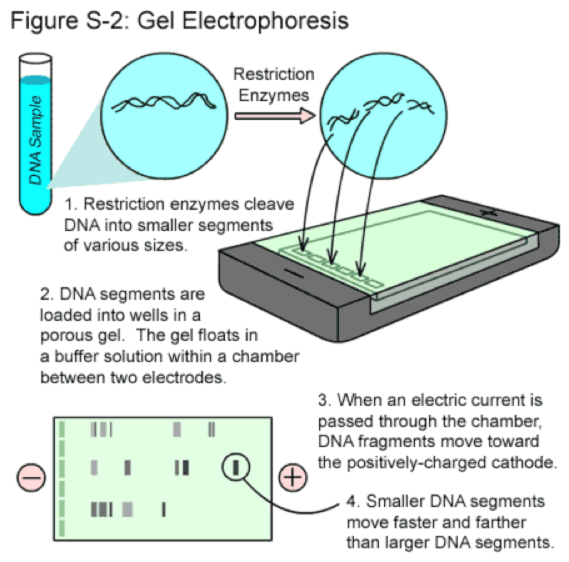
Note: Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA molecules based on their size.
The DNA is usually stained with Ethidium bromide. This stain must be handled with gloves.
The gel is made from an agar. This substance is taken from sea weed or red algae.
It contains pores in the matrix of the agar where the molecules travel through and sorted by size.
DNA molecular weight markers are DNA fragments/bands with known molecular sizes.
This is used to determine the sizes of the unknown strands in your DNA sample.
These markers can be placed in the first or last well.
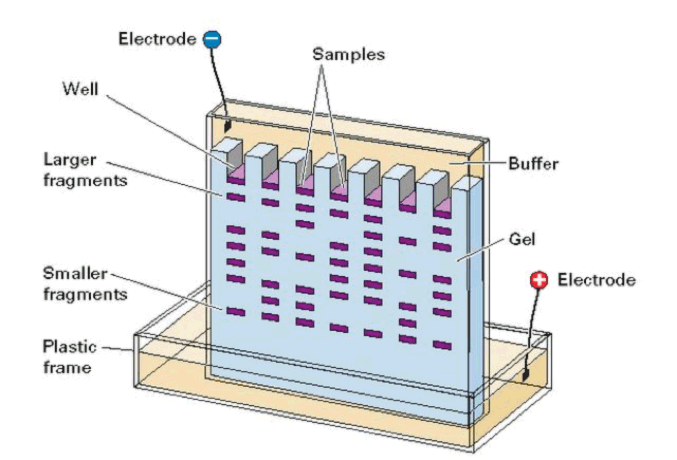
The wells are the spaces at the top of the gel where the dyed DNA fragments are loaded by a pipette.
These spaces can be referred to as the “starting gates”.
The holes in the wells are created by a gel comb.
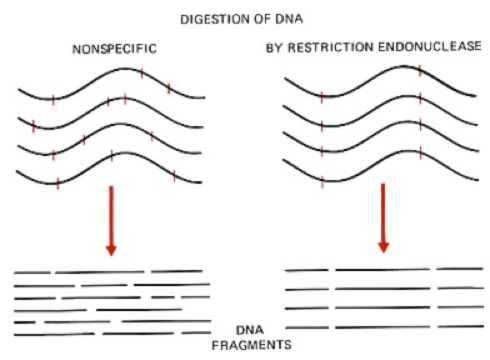
Restrictions enzymes are enzymes found in bacteria that cut DNA at specific nucleotide sequences.
Therefore, there are many different restriction enzymes made by bacteria that can cut DNA fragments at different locations.
Some examples of restriction enzymes are
- EcoRI cuts the DNA sequence between G/A
- HindIIl cuts the DNA sequence between A/A
When powered on with the electrodes, the electrical current flows through the gel from the negative to the positive pole.
A buffer solution added helps with the electrical flow to occur.
The smaller DNA bands travel faster because they have a lower molecular weight. These strands are found lower in the gel.
DNA molecules are negatively charged.
The larger bands travel slower and are found higher up in the gel.
When powered off, the DNA bands will fluoresce in UV light and the band sizes can be estimated. If the machine is not shut off,
the bands will run off the gel.
Restriction Enzymes
Gel Electrophoresis Steps
Electrophoresis Sample Example & Results
- What method is used to sort and measure DNA strands?
- What tool is used in the gel mold to create “holes” for loading the DNA? To load DNA into the gel?
- What direction do the DNA bands migrate towards?
- Describe how are the DNA bands are separated by the gel?
- DNA is colorless, so what is used to make the DNA visible in the gel?
- What is used to cut the DNA strands at specific locations?
- What is the primary reason for conducting this lab procedure?
- What charge does a DNA molecules have?
- Why is the buffer solution added to the gel?
- What is the purpose for the use of DNA molecular weight markers?
Answers:
- Gel electrophoresis
- A gel comb. A pipette
- From the negative pole towards the positive pole.
- The larger DNA fragments travel slower through the pores of the gel and are found higher up on the gel.
The smaller DNA fragments are faster and found toward the bottom of the gel.
- A dye is used to stain the DNA. The dye is called Ethidium bromide.
- Restriction enzymes
- To determine the size of the DNA fragment.
- DNA molecules are negatively charged.
- To aid with the electrical conduction.
- DNA molecular weight markers are used because their known sizes will help you estimate the sizes of the unknown DNA bands.
|


